Core Development Concepts > Background Tasks
How Background Tasks Work?
You will learn about Background Tasks, how to create new definitions, how to trigger them and how to handle the task run.
This feature is available since Webiny v5.39.0.
- how Background Tasks work
- what are the states in Background Task Step Function
- what is the functionality of each state
Overview
A Background Task lifecycle is as follows:
- A user triggers the task either via GraphQL API mutation or via the code.
- As soon as the task is triggered, Webiny sends an EventBridge Event with task information: task ID and task definition identifier.
- The EventBridge triggers the Step Function.
- The Step Function runs the Lambda function in a loop until the task is done.
Step Function Definition
We defined our Step Function as simple as possible, with a lot of error handling, as we did not want to have complex logic in the Step Function itself.
The Pulumi definition for the Step Function is available here
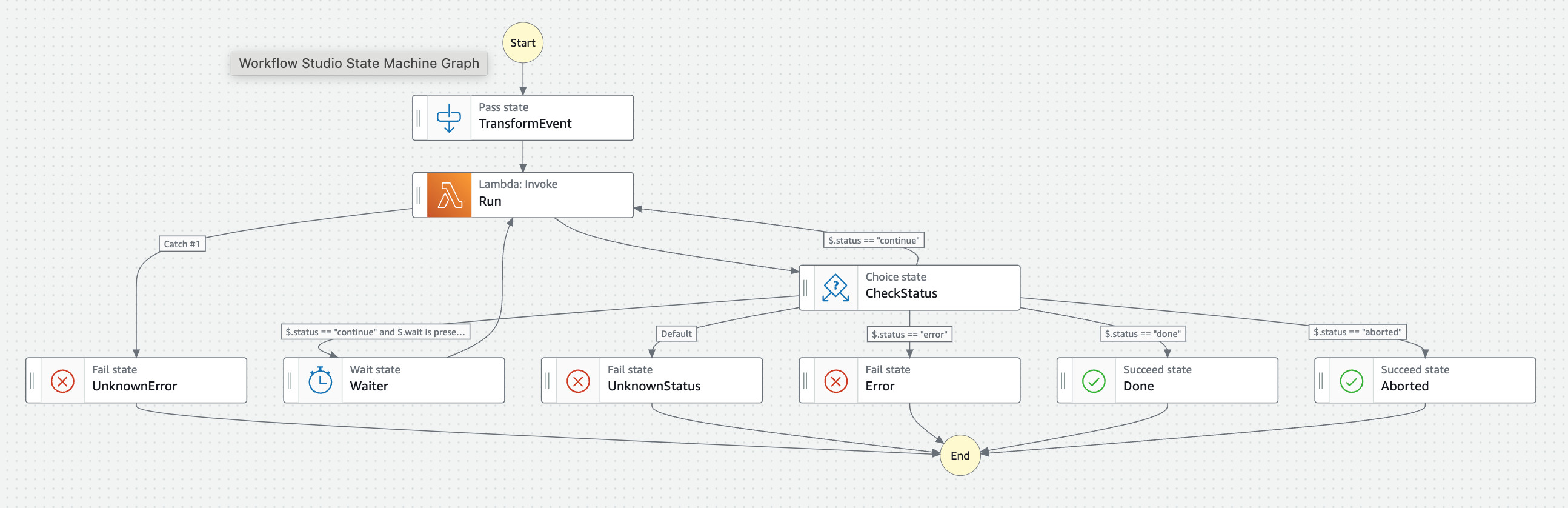 Background Task Step Function Definition
Background Task Step Function DefinitionStep Function States
TransformEvent
This is the first state in our Step Function, and it is responsible for transforming the EventBridge Event into the Background Task Lambda handler input.
This state is required as we want to have simple Background Task Lambda handler input, without any additional information. This is what the Step Function receives from the EventBridge:
and this is what we need to run a Background Task Lambda handler:
Basically, this state is responsible for removing all the unnecessary information from the EventBridge Event.
Run
This state is responsible for running the Background Task Lambda. It runs the Lambda, with the input from the previous state - either TransformEvent or previous Run (Wait) state, and waits for the response.
When the state receives a response from the Lambda handler, it is sent to the CheckStatus state.
CheckStatus
This state is responsible for checking the status of the Background Task Lambda Handler response.
Possible response statuses are:
- done
- error
- aborted
- continue
Done Status
This status signalizes that the Background Task Lambda handler has finished its job and that the Step Function will finish, in a success state.
Error Status
This status signalizes that the Background Task Lambda handler has finished its job with an error and that the Step Function will finish, in an error state.
Aborted Status
This status signalizes that the Background Task Lambda handler has finished its job with an abort and that the Step Function will finish, in an abort state.
Continue Status
This status signalizes that the Background Task Lambda handler has not finished its job and that the Step Function should continue running the Lambda handler.
When user ends current execution of the Background Task Lambda handler, they can also include a waiting time for the next handler run. This can be used when the task needs to wait for some external service to finish its job, before the next handler run. The task must contain the logic for checking if the external service has finished its job, and continue the task execution accordingly.
UnknownError
This state is called when the Step Function Background Task Lambda handler has an unknown error (in the Run state).
This should not happen as the Webiny code always returns a proper response, and everything is wrapped in a try/catch block - with the error response in the catch block.
But, if it happens, for some unknown reason (probably during the development phase), the Step Function will finish in an error state.
UnknownStatus
This state is called when the Step Function Background Task Lambda handler returns an unknown status, and the CheckStatus state determines that the status is unknown.
This should not happen as the Webiny code gives all the tools to the user to return a proper response, and everything is wrapped in a try/catch block - with the error response in the catch block.
But, if it happens, for some unknown reason, the Step Function will finish in an error state.
Error
This state is called when the Step Function Background Task Lambda handler returns an error status, and the CheckStatus state determines that the status is error.
The Step Function will finish in an error state.
Done
This state is called when the Step Function Background Task Lambda handler returns a done status, and the CheckStatus state determines that the status is done.
The Step Function will finish in a success state.
Aborted
This state is called when the Step Function Background Task Lambda handler returns an abort status, and the CheckStatus state determines that the status is aborted.
The Step Function will finish in a success state, as the abort state was triggered by the user.
Background Task Lambda Handler
The Background Task Lambda is deployed with the same code as our GraphQL API Lambda code, with an exception of having more memory assigned.
This way all of your custom code is deployed within the Background Task Lambda as well.
The response of the Background Task Lambda handler is plain JSON, with the following structure:
Users should worry not about the response structure as it is only used internally by the Background Task handler.